开始 🚀
我这里使用 vue3 实现瀑布流+虚拟列表,实现效果可以看这里。
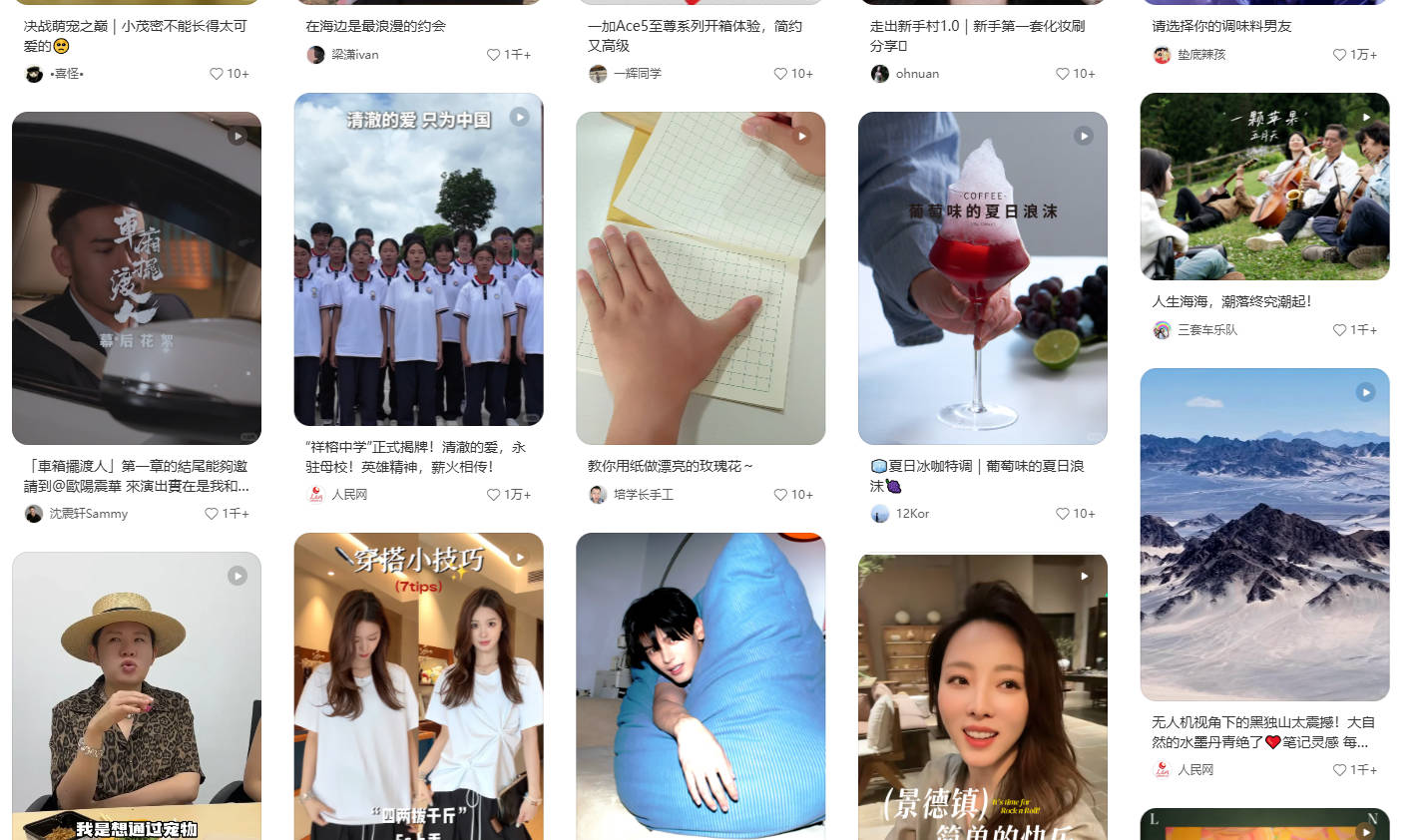
什么是瀑布流?🌊
什么是瀑布流,瀑布流是一种常用于展示不等高内容块的网页布局方式,其特点是:
从上往下填充,优先放到当前最短的那一列。
像下面小红书这样
css 实现 🎨
首先纯 css 就可以实现类似上面的效果,如下面的代码
<div class="p-10 columns-3 lg:columns-5">
<div class="h-[100px] bg-red-100 break-inside-avoid mb-4">1</div>
<div class="h-[120px] bg-blue-100 break-inside-avoid mb-4">2</div>
<div class="h-[50px] bg-slate-200 break-inside-avoid mb-4">3</div>
<div class="h-[90px] bg-orange-200 break-inside-avoid mb-4">4</div>
<div class="h-[40px] bg-yellow-100 break-inside-avoid mb-4">5</div>
<div class="h-[180px] bg-pink-100 break-inside-avoid mb-4">6</div>
<div class="h-[180px] bg-gray-100 break-inside-avoid mb-4">7</div>
</div>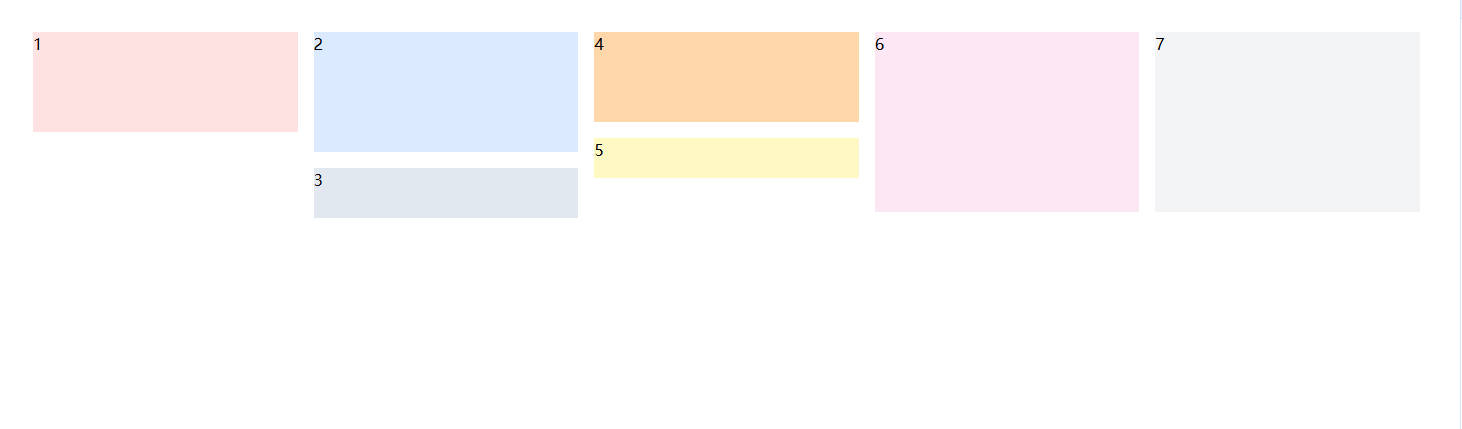
这种方式虽然简单直观,但它是“列优先”填充,而不是我们预期中的“高度最短列优先”。所以当我们需要更精准控制(比如配合虚拟列表)时,CSS 方式就不太够用了。🙅♂️
js 实现 🧩
我们通过 JavaScript 来实现更灵活、可控的瀑布流布局。核心逻辑:
- 获取容器宽度,计算每个卡片宽度;
- 通过响应式断点适配不同列数;
- 根据图片宽高比 & 文本内容动态计算卡片高度;
- 每张卡片插入当前“最短”的列中;
- 用
transform进行绝对定位,性能更优;
布局
布局我们分为容器,列表,列表项三个部分
<div
class="waterfall-container w-full h-full overflow-x-hidden overflow-y-auto"
>
<div class="waterfall-list relative">
<div
class="waterfall-item absolute top-0 left-0 transition-transform duration-300 overflow-hidden will-change-transform"
>
<slot :item="item"></slot>
</div>
</div>
</div>TIP
container 部分要设置超出滚动,子项通过绝对定位统一在左上角,后面通过 translate3d 来实现偏移,再设置插槽来显示内容。
参数定义
- 因为我们是封装的组件,所以要配置一些参数让用户传入。
interface IItem {
id: number;
url: string;
date: Record<string, any>;
frontmatter: Record<string, any>;
}
interface IBreakpoint {
[key: string]: {
columns: number;
gap: number;
};
}
const props = defineProps<{
list: IItem[];
gap: number;
columns: number;
breakPoint?: IBreakpoint;
}>();TIP
list 是列表数据,这里的 id 要设置列表的索引值,后面取数据时要用到。gap 是列表项之间的间距,columns 是列数,breakPoint 是响应式的配置,当屏幕宽度小于某个值时,列数会改变。
- 然后是定义一些变量,用来存储卡片的数据和每一列的高度。
interface ICardPosition {
imageHeight: number;
width: number;
height: number;
x: number;
y: number;
}
const state = reactive({
cardWidth: 0,
cardPosition: [] as ICardPosition[],
columnHeight: [] as number[],
});TIP
cardWidth 是卡片的宽度,cardPosition 存储这卡片的图片高度,卡片宽高和 x,y 的偏移量,columnHeight 是每一列的高度。
获取列数和间距
因为我们是响应式的,所以要根据屏幕宽度来获取用户传入的正确的列数和间距。
const breakPoint = {
560: {
columns: 3,
gap: 10,
},
1024: {
columns: 4,
gap: 20,
},
1280: {
columns: 5,
gap: 20,
},
};通过循环判断获取正确的列数和间距。
const realColumnsAndGap = reactive({
columns: props.columns,
gap: props.gap,
});
const calculateColumnsAndGap = () => {
const breakpoints = props.breakPoint;
const windowWidth = window.innerWidth;
let matched = {
columns: props.columns,
gap: props.gap,
};
let maxMatchedWidth = -1;
if (breakpoints) {
Object.keys(breakpoints).forEach((bp) => {
const bpNum = Number(bp);
if (windowWidth >= bpNum && bpNum > maxMatchedWidth) {
maxMatchedWidth = bpNum;
matched = breakpoints[bpNum];
}
});
}
if (matched) {
realColumnsAndGap.columns = matched.columns;
realColumnsAndGap.gap = matched.gap;
} else {
realColumnsAndGap.columns = props.columns;
realColumnsAndGap.gap = props.gap;
}
};如果没传响应式配置则用默认的 columns 和 gap。
计算卡片的宽度
获取到列数和间距后,就可以通过容器的宽度来计算卡片的宽度了。
这里我们定义个 ref 绑定 container
const containerRef = ref<HTMLDivElement | null>(null);
const calculateCardWidth = () => {
if (!containerRef.value) return;
const containerWidth = containerRef.value.clientWidth;
state.cardWidth =
(containerWidth - realColumnsAndGap.gap * (realColumnsAndGap.columns - 1)) /
realColumnsAndGap.columns;
};TIP
gap 的数量是 columns - 1
计算图片高度
这里的图片宽高信息要通过后端返回,不然只能通过前端预加载来获取,但是对于图片多的来说,这样非常耗时间。
const calculateCardImageHeight = () => {
list.value.forEach((item, index) => {
if (!item.frontmatter.pic) return;
const [width, height] = item.frontmatter.picSize.split("x");
const imageHeight = Math.floor((state.cardWidth * height) / width);
state.cardPosition[index] = {
...state.cardPosition[index],
imageHeight,
};
});
};计算卡片高度
首先我们分析下小红书的布局,分为图片、标题、和作者信息。
这里图片的高度我们知道了,作者信息的高度通过元素选择我们可以看到是固定的 20px,所以我们只需要计算标题的高度就可以了。
小红书这里标题分为一行跟两行,我们通过 canvas 的 measureText 可以获取文本的宽度,我们可以拿到这个宽度跟卡片的宽度比较,如果超过卡片的宽度就表示文本会换行显示,直接取两行的高度即可。
我的文章列表也类似小红书的布局,分为图片、标题、简介和发布时间。
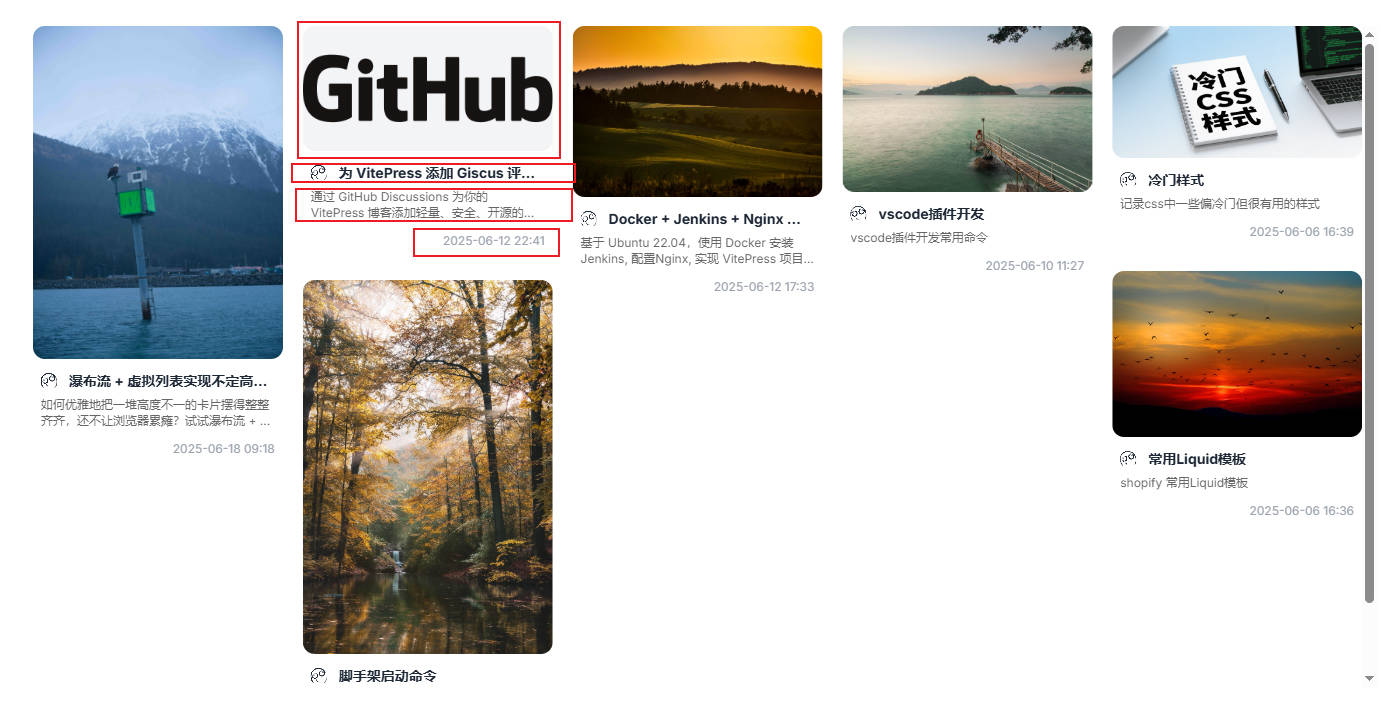
内容区域的边距,标题高度,发布时间高度是固定的,一行简介跟两行简介的高度也是固定的,所以我们可以先定义好变量。
const padding = 24;
const titleHeight = 20;
const oneRowContent = 22;
const twoRowContent = 38;
const timeHeight = 28;首先定义一个隐藏的 canvas,用来测量文本的宽度
<canvas id="canvas" ref="canvasRef" class="hidden"></canvas>接着就可以计算文本宽度
const canvasRef = ref<HTMLCanvasElement | null>(null);
const getTextWidth = (text: string) => {
if (!canvasRef.value || !containerRef.value) return 0;
const ctx = canvasRef.value.getContext("2d");
if (!ctx) return 0;
const style = getComputedStyle(containerRef.value);
ctx.font = `12px ${style.fontFamily}`;
const canvasText = ctx.measureText(text);
return canvasText.width;
};TIP
这里需要注意设置 canvas 的字体样式,我的标题是用的 12px 的字体大小,字体用的默认字体。
获取卡片高度
const getCardHeight = () => {
list.value.forEach((item, index) => {
const padding = 24;
const titleHeight = 20;
const oneRowContent = 22;
const twoRowContent = 38;
const timeHeight = 28;
const contentWidth = getTextWidth(item.frontmatter.desc);
const contentHeight =
contentWidth > state.cardWidth - 16 ? twoRowContent : oneRowContent;
const cardHeight =
padding +
titleHeight +
contentHeight +
timeHeight +
state.cardPosition[index].imageHeight;
});
};获取到卡片的高度信息后,我们需要将信息添加到上面定义的 state.cardPosition 中,同时将信息加入 state.columnHeight 中,方便后面计算卡片的位置。 我们知道瀑布流的布局第一排都是在最顶上,从第二排开始,每个卡片在插入时,要插入最小高度的那一列中,所以我们分两种情况。
- 第一排时
if (index < realColumnsAndGap.columns) {
state.cardPosition[index] = {
...state.cardPosition[index],
width: state.cardWidth,
height: cardHeight,
x:
index % realColumnsAndGap.columns === 0
? 0
: index * (state.cardWidth + realColumnsAndGap.gap),
y: 0,
};
state.columnHeight[index] = cardHeight + realColumnsAndGap.gap;
}TIP
当是最左边一个的时候,x 的值为 0,否则为当前列数乘以卡片宽度加上间距。
- 不是第一排 不是第一排的时候我们要获取最小高度的列和对应的索引值。因为后面需要将高度最大的那一列的值绑定到列表的高度上,所以这里我们定义一个用来获取最大和最小高度列的函数。
const columnStats = computed(() => {
let minIndex = -1;
let minHeight = 0;
let maxHeight = 0;
state.columnHeight.forEach((height, index) => {
// 处理最小值
if (minIndex === -1 || height < minHeight) {
minIndex = index;
minHeight = height;
}
// 处理最大值
if (height > maxHeight) {
maxHeight = height;
}
});
return {
minIndex,
minHeight,
maxHeight,
};
});用获取到的最小高度列的索引值来替换 index,和 y。
const { minIndex, minHeight } = columnStats.value;
state.cardPosition[index] = {
...state.cardPosition[index],
width: state.cardWidth,
height: cardHeight,
x: minIndex * (state.cardWidth + realColumnsAndGap.gap),
y: minHeight,
};
state.columnHeight[minIndex] += cardHeight + realColumnsAndGap.gap;完整的获取卡片高度的代码如下
const getCardHeight = () => {
list.value.forEach((item, index) => {
const padding = 24;
const titleHeight = 20;
const oneRowContent = 22;
const twoRowContent = 38;
const timeHeight = 28;
const contentWidth = getTextWidth(item.frontmatter.desc);
const contentHeight =
contentWidth > state.cardWidth - 16 ? twoRowContent : oneRowContent;
const cardHeight =
padding +
titleHeight +
contentHeight +
timeHeight +
state.cardPosition[index].imageHeight;
if (index < realColumnsAndGap.columns) {
state.cardPosition[index] = {
...state.cardPosition[index],
width: state.cardWidth,
height: cardHeight,
x:
index % realColumnsAndGap.columns === 0
? 0
: index * (state.cardWidth + realColumnsAndGap.gap),
y: 0,
};
state.columnHeight[index] = cardHeight + realColumnsAndGap.gap;
} else {
const { minIndex, minHeight } = columnStats.value;
state.cardPosition[index] = {
...state.cardPosition[index],
width: state.cardWidth,
height: cardHeight,
x: minIndex * (state.cardWidth + realColumnsAndGap.gap),
y: minHeight,
};
state.columnHeight[minIndex] += cardHeight + realColumnsAndGap.gap;
}
});
};最后我们将上面的方法整合进 init 中统一执行,再加监听下 container 的宽度变化,来实现响应式。
const init = () => {
// 1.初始化
state.cardWidth = 0;
state.cardPosition = [];
state.columnHeight = [];
// 2.计算列数和间距
calculateColumnsAndGap();
// 3.根据容器宽度、列数和间距,计算卡片宽度
calculateCardWidth();
// 4.计算图片高度
calculateCardImageHeight();
// 5.计算卡片高度
getCardHeight();
};我们用 ResizeObserver 来监听容器宽度的变化。
// 因为宽度变化是很频繁的,我们封装一个防抖来优化下
const debounce = (fn, delay, immediate = false) => {
let timer;
return function (...args) {
const context = this;
if (timer) clearTimeout(timer);
if (immediate && !timer) {
fn.apply(context, args);
}
timer = setTimeout(() => {
if (!immediate) fn.apply(context, args);
timer = null;
}, delay);
};
};
const debounceInit = debounce(init, 500);
const resizeObserver = new ResizeObserver(() => {
debounceInit();
});在 onMounted 中执行。
onMounted(async () => {
if (!containerRef.value) return;
init();
resizeObserver.observe(containerRef.value);
});
onUnmounted(() => {
containerRef.value && resizeObserver.unobserve(containerRef.value);
});最后通过 v-for 渲染,绑定下样式。
<canvas id="canvas" ref="canvasRef" class="hidden"></canvas>
<div
class="waterfall-container w-full h-full overflow-x-hidden overflow-y-auto"
ref="containerRef"
>
<div
class="waterfall-list relative"
ref="listRef"
:style="{ height: columnStats.maxHeight + 'px' }"
>
<div
class="waterfall-item absolute top-0 left-0 transition-transform duration-300 overflow-hidden will-change-transform"
v-for="item in list"
:key="item.id"
:style="{
width: `${state.cardWidth}px`,
height: `${state.cardPosition[item.id]?.height}px`,
transform: `translate3d(${state.cardPosition[item.id]?.x || 0}px, ${
state.cardPosition[item.id]?.y || 0
}px, 0)`,
}"
>
<slot :item="item"></slot>
</div>
</div>
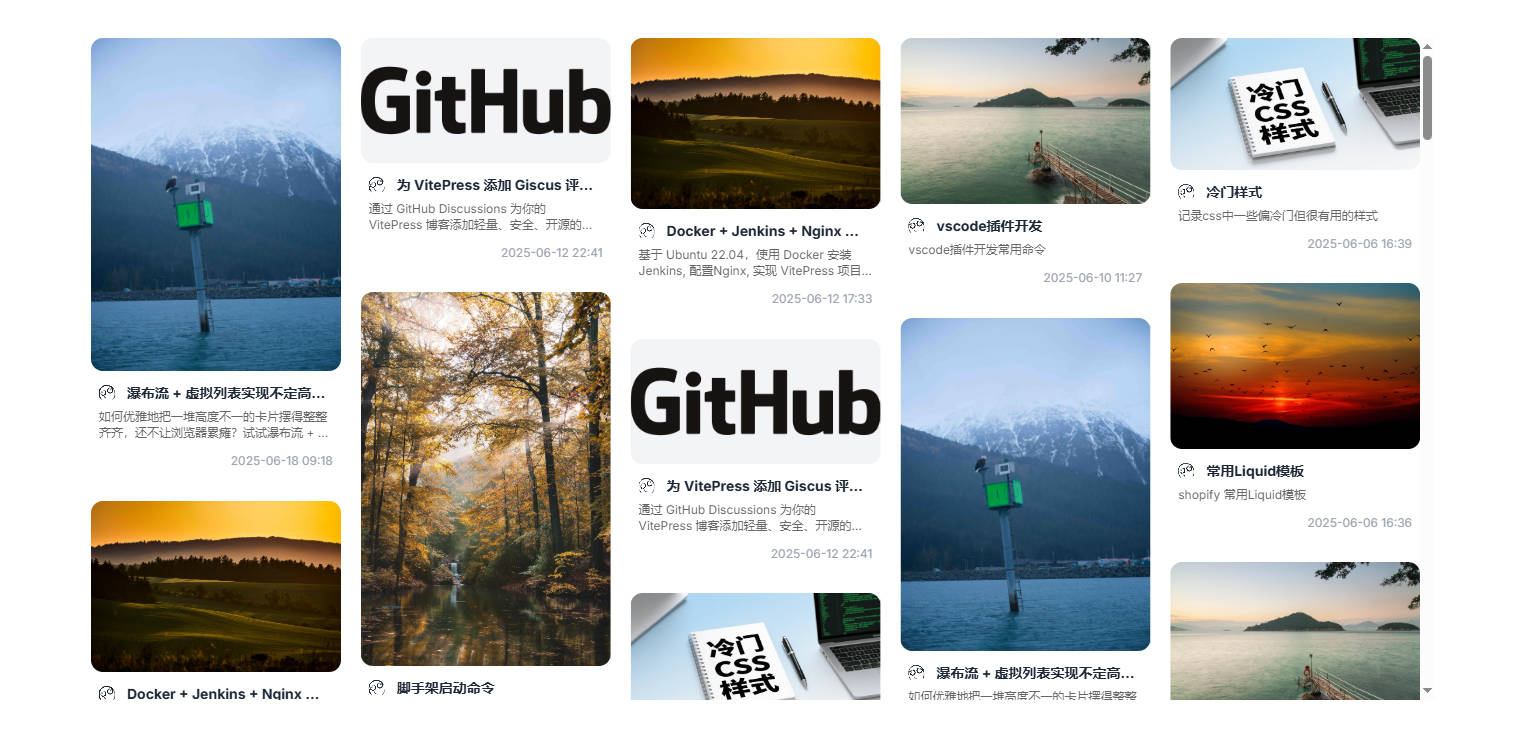
</div>到这瀑布流的效果就做好了,可以来看看效果。
虚拟列表 👀
虚拟列表是一种性能优化技术,用于高效渲染大量数据项的滚动列表,常用于前端开发中。它的核心思想是:
只渲染可视区域内的元素,避免一次性将所有列表项都插入 DOM。

在前面实现瀑布流的时候获取了卡片的位置信息,所以我们结合容器的 scrollTop 和位置信息从 list 中筛选出可见的卡片数组进行渲染。
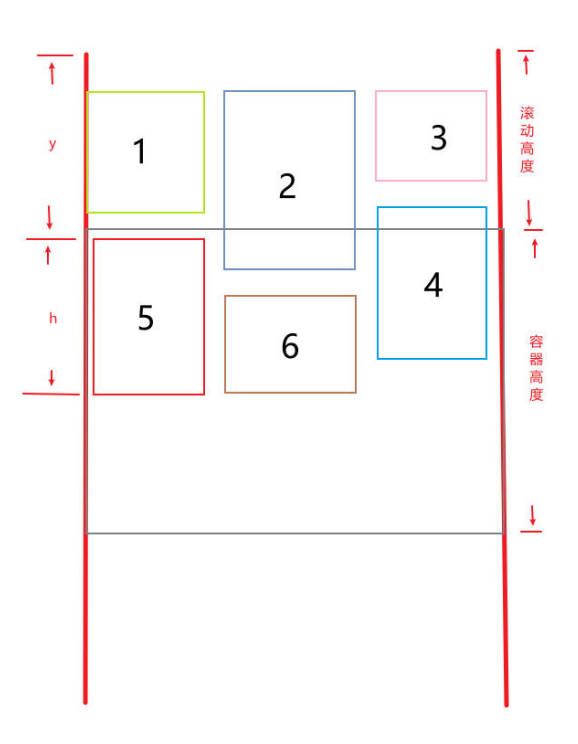
通过上面的图可以得出:
- 当卡片的高度 h + 卡片的 y 大于 容器的滚动高度时,该卡片在容器顶部的下方。
- 当卡片的 y 小于容器的滚动高度 + 容器高度时,该卡片在容器底部上方。
同时满足以上条件的卡片,即为可见的卡片。现在我们就来将满足这两个条件的卡片过滤出来。
同时加入一段缓冲区域,让滚动更丝滑(比如 buffer 高度是容器高度的 50%)。
const visibleCard = ref<IItem[]>([]);
const calculateVisibleCard = () => {
const bufferHeight = containerRef.value
? containerRef.value.clientHeight * 0.5
: 0;
const arr = list.value.filter((_, index) => {
if (state.cardPosition[index] && containerRef.value) {
const h = state.cardPosition[index].height;
const y = state.cardPosition[index].y;
const scrollTop = containerRef.value.scrollTop;
const viewportHeight = containerRef.value.clientHeight;
return (
y + h > scrollTop - bufferHeight &&
y < scrollTop + viewportHeight + bufferHeight
);
}
});
visibleCard.value = arr;
};再将这个方法绑定到滚动事件上,这里放到 requestAnimationFrame 中,来优化性能。
const throttleRAF = (fn) => {
let running = false;
return function () {
if (running) return;
running = true;
requestAnimationFrame(() => {
fn();
running = false;
});
};
};
const throttledCalculateVisibleCard = throttleRAF(calculateVisibleCard);最后 html 中添加滚动事件监听
<canvas id="canvas" ref="canvasRef" class="hidden"></canvas>
<div
class="waterfall-container w-full h-full overflow-x-hidden overflow-y-auto"
ref="containerRef"
@scroll="throttledCalculateVisibleCard"
>
<div
class="waterfall-list relative"
ref="listRef"
:style="{ height: columnStats.maxHeight + 'px' }"
>
<div
class="waterfall-item absolute top-0 left-0 transition-transform duration-300 overflow-hidden will-change-transform"
v-for="item in visibleCard"
:key="item.id"
:style="{
width: `${state.cardWidth}px`,
height: `${state.cardPosition[item.id]?.height}px`,
transform: `translate3d(${state.cardPosition[item.id]?.x || 0}px, ${
state.cardPosition[item.id]?.y || 0
}px, 0)`,
}"
>
<div class="animate-box">
<slot :item="item"></slot>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>这里嵌套了个 animate-box 的 div 用来添加渐入的动画效果。
.animate-box {
animation: MoveAnimate 0.5s;
}
@keyframes MoveAnimate {
from {
opacity: 0;
transform: translateY(200px);
}
to {
opacity: 1;
transform: translateY(0);
}
}最后实现的效果,注意右侧 dom 的变化。

